
 |
Home | Libraries | People | FAQ | More |
Copyright © 2003-2013 Jan Gaspar
Distributed under the Boost Software License, Version 1.0. (See accompanying file LICENSE_1_0.txt or copy at http://www.boost.org/LICENSE_1_0.txt)
Table of Contents
![[Note]](../../doc/src/images/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
A printer-friendly PDF version of this manual is also available. |
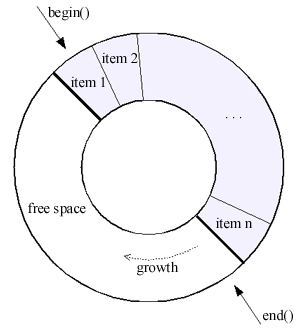
A Circular Buffer.
The term circular buffer (also called a ring or cyclic buffer) refers to an area in memory which is used to store incoming data. When the buffer is filled, new data is written starting at the beginning of the buffer and overwriting the old.
boost::circular_buffer
is a STL compliant container.
It is a kind of sequence similar to std::list or std::deque. It supports random access iterators, constant time insert and erase operations at the beginning or the end of the buffer and interoperability with std algorithms.
The circular_buffer is
especially designed to provide fixed capacity
storage. When its capacity is exhausted, newly inserted elements will cause
elements to be overwritten, either at the beginning or end of the buffer (depending
on what insert operation is used).
The circular_buffer only
allocates memory when created, when the capacity is adjusted explicitly, or
as necessary to accommodate resizing or assign operations.
There is also a circular_buffer_space_optimized
version available.
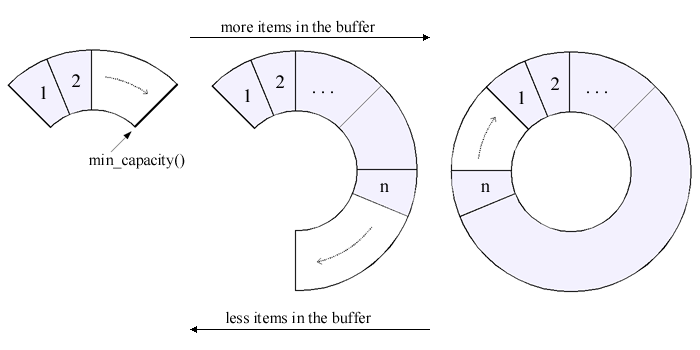
circular_buffer_space_optimized
is an adaptation of the circular_buffer
which does not allocate memory all at once when created,
instead it allocates memory as needed.
The predictive memory allocation is similar to typical std::vector
implementation. Memory is automatically freed as the size of the container
decreases.
The memory allocation process of the space-optimized circular buffer. The
min_capacity
of the capacity controller represents the minimal guaranteed amount of allocated
memory. The allocated memory will never drop under this value. The default
value of the min_capacity is
set to 0. The min_capacity
can be set using the constructor parameter ()
capacity_control or the function set_capacity.
The space-optimized version is, of course, a little slower.