QTextTableFormat Class
The QTextTableFormat class provides formatting information for tables in a QTextDocument. More...
| Header: | #include <QTextTableFormat> |
| CMake: | find_package(Qt6 REQUIRED COMPONENTS Gui) target_link_libraries(mytarget PRIVATE Qt6::Gui) |
| qmake: | QT += gui |
| Inherits: | QTextFrameFormat |
- List of all members, including inherited members
- QTextTableFormat is part of Rich Text Processing APIs and Implicitly Shared Classes.
Note: All functions in this class are reentrant.
Public Functions
| QTextTableFormat() | |
| Qt::Alignment | alignment() const |
| bool | borderCollapse() const |
| qreal | cellPadding() const |
| qreal | cellSpacing() const |
| void | clearColumnWidthConstraints() |
| QList<QTextLength> | columnWidthConstraints() const |
| int | columns() const |
| int | headerRowCount() const |
| bool | isValid() const |
| void | setAlignment(Qt::Alignment alignment) |
| void | setBorderCollapse(bool borderCollapse) |
| void | setCellPadding(qreal padding) |
| void | setCellSpacing(qreal spacing) |
| void | setColumnWidthConstraints(const QList<QTextLength> &constraints) |
| void | setHeaderRowCount(int count) |
Detailed Description
A table is a group of cells ordered into rows and columns. Each table contains at least one row and one column. Each cell contains a block. Tables in rich text documents are formatted using the properties defined in this class.
Tables are horizontally justified within their parent frame according to the table's alignment. This can be read with the alignment() function and set with setAlignment().
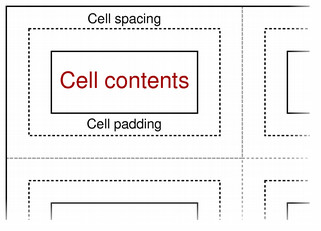
Cells within the table are separated by cell spacing. The number of pixels between cells is set with setCellSpacing() and read with cellSpacing(). The contents of each cell is surrounded by cell padding. The number of pixels between each cell edge and its contents is set with setCellPadding() and read with cellPadding().
The table's background color can be read with the background() function, and can be specified with setBackground(). The background color of each cell can be set independently, and will control the color of the cell within the padded area.
The table format also provides a way to constrain the widths of the columns in the table. Columns can be assigned a fixed width, a variable width, or a percentage of the available width (see QTextLength). The columns() function returns the number of columns with constraints, and the columnWidthConstraints() function returns the constraints defined for the table. These quantities can also be set by calling setColumnWidthConstraints() with a list containing new constraints. If no constraints are required, clearColumnWidthConstraints() can be used to remove them.
See also QTextTable, QTextTableCell, and QTextLength.
Member Function Documentation
QTextTableFormat::QTextTableFormat()
Constructs a new table format object.
Qt::Alignment QTextTableFormat::alignment() const
Returns the table's alignment.
See also setAlignment().
bool QTextTableFormat::borderCollapse() const
Returns true if borderCollapse is enabled.
See also setBorderCollapse().
qreal QTextTableFormat::cellPadding() const
Returns the table's cell padding. This describes the distance between the border of a cell and its contents.
See also setCellPadding().
qreal QTextTableFormat::cellSpacing() const
Returns the table's cell spacing. This describes the distance between adjacent cells.
See also setCellSpacing().
void QTextTableFormat::clearColumnWidthConstraints()
Clears the column width constraints for the table.
See also columnWidthConstraints() and setColumnWidthConstraints().
QList<QTextLength> QTextTableFormat::columnWidthConstraints() const
Returns a list of constraints used by this table format to control the appearance of columns in a table.
See also setColumnWidthConstraints().
int QTextTableFormat::columns() const
Returns the number of columns specified by the table format.
int QTextTableFormat::headerRowCount() const
Returns the number of rows in the table that define the header.
See also setHeaderRowCount().
bool QTextTableFormat::isValid() const
Returns true if this table format is valid; otherwise returns false.
void QTextTableFormat::setAlignment(Qt::Alignment alignment)
Sets the table's alignment.
See also alignment().
void QTextTableFormat::setBorderCollapse(bool borderCollapse)
Enabling borderCollapse will have the following implications:
- The borders and grid of the table will be rendered following the CSS table
border-collapse:collapserules - Setting the
borderproperty to a minimum value of1will render a one pixel solid inner table grid using the borderBrush property and an outer border as specified - The various border style properties of QTextTableCellFormat can be used to customize the grid and have precedence over the border and grid of the table
- The cellSpacing property will be ignored
- For print pagination:
- Columns continued on a page will not have their top cell border rendered
- Repeated header rows will always have their bottom cell border rendered
With borderCollapse disabled, cell borders can still be styled using QTextTableCellFormat but styling will be applied only within the cell's frame, which is probably not very useful in practice.
See also borderCollapse(), setBorder(), setBorderBrush(), setBorderStyle(), and QTextTableCellFormat.
void QTextTableFormat::setCellPadding(qreal padding)
Sets the cell padding for the table. This determines the distance between the border of a cell and its contents.
See also cellPadding().
void QTextTableFormat::setCellSpacing(qreal spacing)
Sets the cell spacing for the table. This determines the distance between adjacent cells.
This property will be ignored if borderCollapse is enabled.
See also cellSpacing().
void QTextTableFormat::setColumnWidthConstraints(const QList<QTextLength> &constraints)
Sets the column width constraints for the table.
See also columnWidthConstraints() and clearColumnWidthConstraints().
void QTextTableFormat::setHeaderRowCount(int count)
Declares the first count rows of the table as table header. The table header rows get repeated when a table is broken across a page boundary.
See also headerRowCount().